Comment accéder aux MetaData d'une classe en utilisant Java ?
Pour obtenir les métadonnées , nous utilisons l'API de réflexion Java. La classe de réfracteur Java fournit les méthodes pour obtenir les métadonnées d'une classe. Ici, nous allons utiliser les méthodes suivantes.
- class.forName()
Cette méthode charge une classe qui est fournie en paramètre, si la classe n'est pas trouvée, une erreur sera générée. - isInterface()
Cette fonction vérifie si une classe est une interface ou non et renvoie une valeur booléenne. - getDeclaredFields()
Ceci renvoie le nom de tous les champs d'une classe. - getDeclaredMethods()
Ceci renvoie le nom de toutes les méthodes d'une classe. - getDeclaredConstructor()
Cela renvoie tous les noms de constructeur d'une classe.
Comprenons-les plus clairement par cet exemple. Ici, nous avons un nom de classe Product avec trois champs et une interface nommée NoteBook.
package logicProgramming;
/*
* In This Program We are Going to Get Meta Data Of Running Class
* And Going To Examine And Change The Behavior Of Class
*/
import java.lang.Class;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
//an interface
interface NoteBook
{
int bookId=100;
}
//a class
class Product{
private int productId;
private String name;
public long price;
//constructor
public Product(int productId,String name,long price)
{
this.productId=productId;
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
}
//constructor
public Product()
{}
//this function prints the data of the object
public void putProduct()
{System.out.println("ProductId :"+this.productId+"\nName :"+this.name+"\nPrice"+this.price);}
public String toString()
{
return("ProductId :"+this.productId+"\nName :"+this.name+"\nPrice"+this.price);
// to return object so that object values are printed rather
//than it's hexadecimal address
}
}
//main class
public class ExClassMetaData_ReflectionAPI_JAVA {
public static void main(String arg[])
{
try
{
//Class.forName(ClassName) Use For Loading The Class
Class cs=Class.forName("logicProgramming.Product");
System.out.println(cs.getName()); //getName() function is getting the name of the class
//getClass() Is also used To get The meta Data Of Class
System.out.println();
Product P=new Product();
Class pcls=P.getClass();//getting the meta data of Product class
System.out.println(pcls.getName());
System.out.println();
//public boolean isInterface() tells that whether
//the current class is Interface or a Simple Class
System.out.println(Class.forName("logicProgramming.Product").isInterface());
//Book Is a Interface so It Will print True...
System.out.println();
System.out.println(Class.forName("logicProgramming.NoteBook").isInterface());
//public Field[] getDeclaredFields()
//returns an array of name of all fields of this class.
Field fields[] =cs.getDeclaredFields();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Fields Of product Class");
//loop to print the fields name of the class
for(int i=0;i<fields.length;i++)
{System.out.println(fields[i]);}
//public Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
//returns an array of name of all methods of this class.
Method methods[]=pcls.getDeclaredMethods();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Methods Of product Class");
//loop to print the methods name of the class
for(int i=0;i<methods.length;i++)
{System.out.println(methods[i]);}
//public Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors()
//returns the total number of constructors of this class.
Constructor<Product> constructors[]=pcls.getDeclaredConstructors();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Constructors Of product Class");
//loop to print the constructor name of the class
for(int i=0;i<constructors.length;i++)
{System.out.println(constructors[i]);}
}
catch(ClassNotFoundException e)
{
System.out.println(e);
}
}
}
Sortie
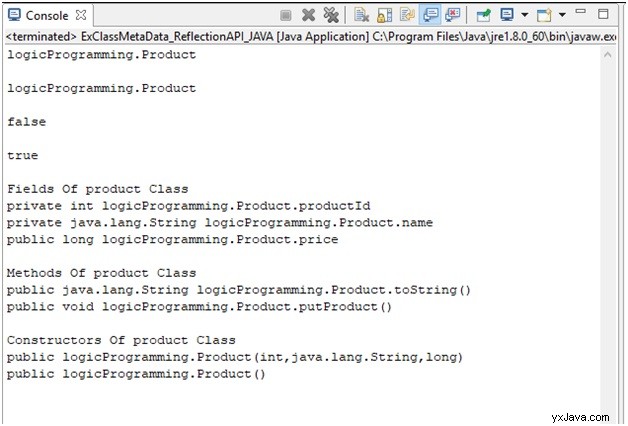
Ici, nous avons toutes les métadonnées de la classe.
Remarque : "programmation logique" est le nom du package, remplacez-le par le nom de votre package